Imagine if blood were a bustling city, plasma would be its bustling main avenue. It’s not just any street; it’s packed with all sorts of important stuff constantly moving around, keeping the city alive and thriving. Plasma isn’t like the solid or liquid things you usually see around you. It’s more like a fluid, but not just plain water. It’s a bit like a special soup made mostly of water but also contains lots of tiny ingredients like salts, proteins, hormones, gases, and even waste products.
Serving as the body’s delivery system, plasma ensures the distribution of nutrients and oxygen to every corner, facilitating cellular function and vitality while expelling waste materials. Moreover, plasma acts as the body’s vigilant security force, armed with specialized proteins that ward off invading pathogens, safeguarding against infections and illnesses.
Furthermore, in times of injury, plasma steps in as a rapid-response team, initiating clot formation to staunch bleeding and kickstart the healing process. In essence, plasma serves as the lifeblood of the body, orchestrating vital functions and fortifying resilience. Understanding its intricate workings fosters appreciation for its indispensable role in maintaining health and vitality.
Medical Applications of Plasma
In the realm of healthcare, plasma proves to be a versatile resource with various applications that benefit patients in different ways. Let’s dive into some of the key medical uses of plasma.
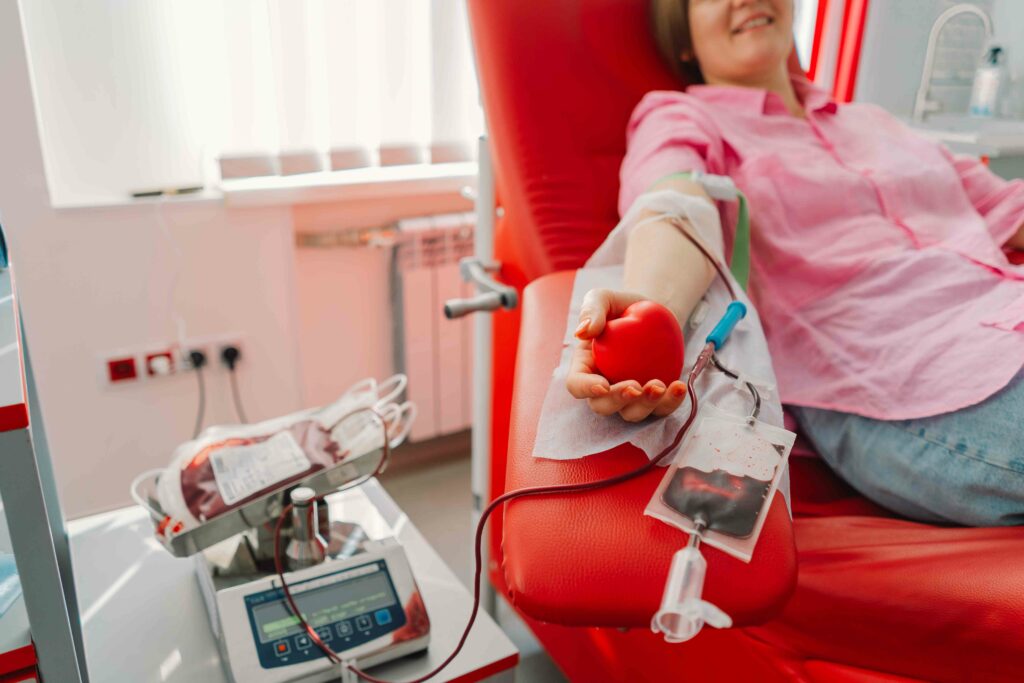
Blood Transfusions and Plasma Products
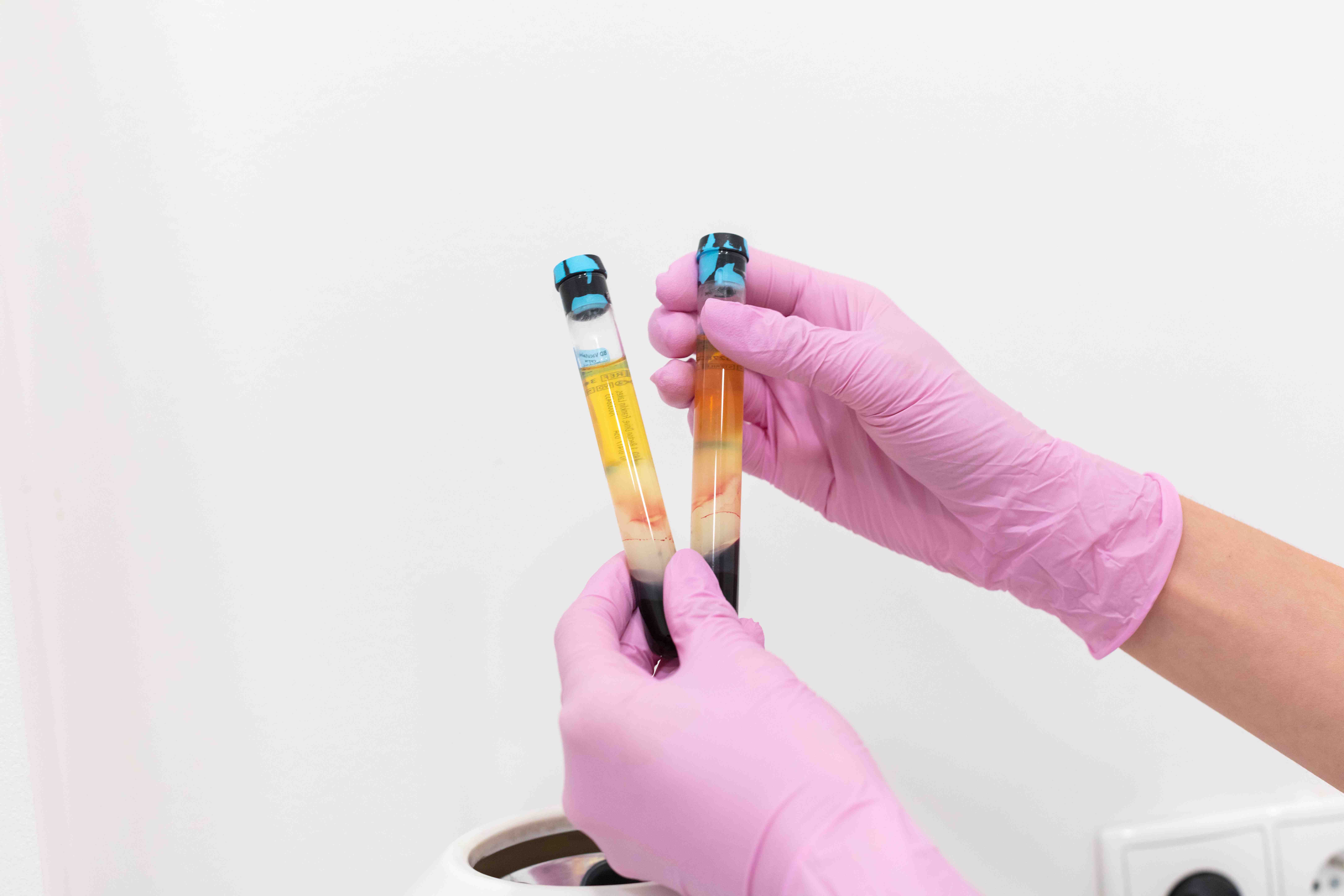
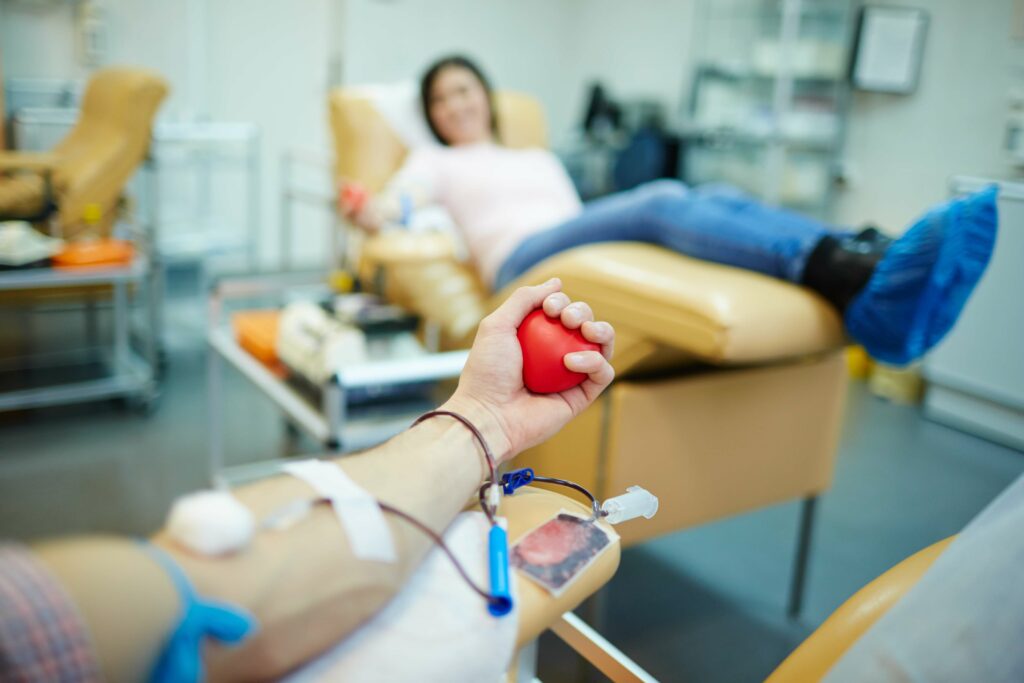
Blood transfusions, a common medical procedure, rely on plasma’s crucial role. In cases of significant blood loss from injury or surgery, transfusions become necessary to replenish blood supply. Plasma, rich in essential proteins and clotting factors, aids in restoring balance and clotting to prevent excessive bleeding when transfused alongside red blood cells. Additionally, plasma serves as a source for valuable plasma-derived products, including immunoglobulins and clotting factors like factor VIII and IX. These products are vital for treating conditions like hemophilia and infections, often proving lifesaving in emergencies or as ongoing treatments.
Plasma Exchange Therapy
Plasma exchange therapy, also known as plasmapheresis, is a specialized medical procedure used to treat various autoimmune and neurological disorders. During this procedure, the patient’s blood is circulated through a machine that separates plasma from other blood components. The plasma, which may contain harmful antibodies or toxins contributing to the patient’s condition, is then removed and replaced with donor plasma or a plasma substitute. This process helps remove harmful substances from the bloodstream, alleviating symptoms and improving the patient’s condition.
Plasma in Regenerative Medicine
In the exciting field of regenerative medicine, plasma holds promise for promoting tissue repair and regeneration. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP), a concentrated form of plasma containing a high concentration of platelets, growth factors, and other bioactive molecules, is gaining traction as a treatment for various musculoskeletal injuries, such as tendon and ligament injuries, osteoarthritis, and even skin rejuvenation. PRP injections stimulate the body’s natural healing processes, accelerating tissue repair and regeneration, and offering a non-invasive alternative to traditional therapies.
Industrial and Scientific Applications of Plasma
Beyond its crucial role in healthcare, plasma finds extensive applications in various industries and scientific fields, driving innovation and advancing technology in remarkable ways. Let’s explore some of the key industrial and scientific uses of plasma.
Plasma Cutting and Welding
Plasma cutting and welding are indispensable processes in metal fabrication and construction industries. Plasma cutting involves using a high-velocity jet of ionized gas, or plasma, to slice through electrically conductive materials with precision and efficiency. This method is favored for its ability to cut through thick metals quickly and cleanly, making it essential in manufacturing, automotive, and construction sectors. Similarly, plasma welding utilizes controlled plasma arcs to join metal components together seamlessly, offering superior weld quality and productivity compared to conventional welding techniques.
Plasma in Semiconductor Manufacturing
In the realm of semiconductor manufacturing, plasma plays a pivotal role in fabricating microelectronic devices and integrated circuits. Plasma etching, a key process in semiconductor fabrication, selectively removes material from semiconductor substrates to create intricate patterns and structures at the nanoscale level. Plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) is another essential technique utilized to deposit thin films of various materials onto semiconductor surfaces with high precision and uniformity, enabling the production of advanced semiconductor devices with enhanced performance and functionality.
Plasma Sterilization
Plasma sterilization emerges as a highly effective method for decontaminating medical instruments, pharmaceuticals, and packaging materials. Unlike traditional methods relying on heat or chemicals, it utilizes low-temperature plasma from gases like hydrogen peroxide or oxygen to eliminate pathogens. This gentle yet potent technique boasts advantages like compatibility with heat-sensitive materials, shorter cycle times, and superior penetration into complex geometries.
Ideal for healthcare, pharmaceutical, and biotechnology industries, plasma sterilization underscores its versatility and efficacy across diverse fields. From metal fabrication to semiconductor manufacturing and sterilization, these applications highlight plasma’s integral role in innovation. With advancing technology, plasma-based processes are poised to shape the future of various industries.
Future Perspectives and Emerging Trends
Looking ahead, the future of plasma research holds promising opportunities and potential breakthroughs that could revolutionize healthcare and scientific innovation. Let’s delve into two emerging trends that are poised to shape the landscape of plasma applications in the coming years.
Plasma-Based Cancer Therapies
Plasma-based cancer therapies offer a cutting-edge approach to battling cancer, ushering in new avenues for targeted treatment and improved patient outcomes. Researchers explore plasma’s potential, especially cold atmospheric plasma (CAP), for selectively targeting and eliminating cancer cells while preserving healthy tissue. CAP generates a unique blend of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species, alongside electric fields, exerting potent anti-cancer effects by inducing apoptosis, inhibiting proliferation, and disrupting the tumor microenvironment.
Moreover, plasma-based therapies show promise in overcoming resistance to conventional treatments like chemotherapy and radiation therapy, either by sensitizing cancer cells or enhancing efficacy. CAP’s non-thermal nature enables precise tumor targeting, minimizing damage to surrounding tissues and reducing side effects. As research progresses, plasma-based cancer therapies may integrate into personalized treatment regimens, offering renewed hope to patients with challenging malignancies.
Plasma Medicine
Plasma medicine, an interdisciplinary field, explores plasma’s therapeutic potential beyond cancer. From chronic wounds to dermatological disorders, plasma-based therapies offer versatile solutions. Cold atmospheric plasma (CAP) devices, known for antimicrobial properties and wound healing, gain attention.
In dermatology, plasma skin resurfacing and plasma-induced photodynamic therapy show promise in treating acne, psoriasis, and aging. Plasma-activated liquids (PALs) offer innovative healthcare approaches, replacing conventional antimicrobial agents. Advancing research and evolving technology position plasma medicine to revolutionize clinical practice and enhance patient care across medical specialties.
Conclusion
In conclusion, plasma’s diverse applications underscore its profound impact across healthcare, industry, and scientific research. From vital roles in blood transfusions and medical therapies to cutting-edge technologies like plasma cutting and semiconductor manufacturing, plasma shapes our world remarkably. As we advance, integrating plasma-based technologies promises innovation, productivity enhancements, and improved global quality of life. Ongoing research and technological advancements expand the horizons of plasma applications, offering limitless opportunities for exploration and progress. Let’s continue to harness plasma’s power to address global challenges, drive scientific inquiry, and unravel the mysteries of the universe, propelling humanity towards a brighter future.